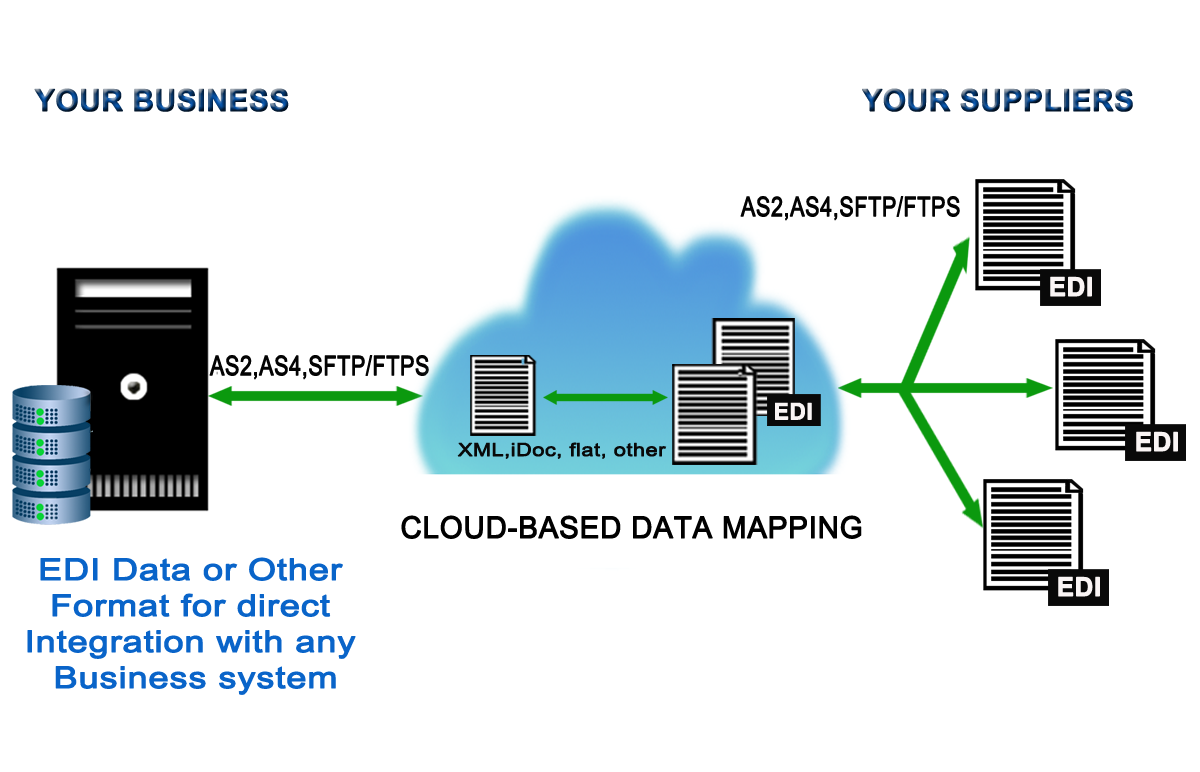
EDI, which stands for electronic data interchange, is the intercompany communication of business documents in a standard format. The simple definition of EDI is a standard electronic format that replaces paper-based documents such as purchase orders or invoices. EDI helps businesses and teams save time and money by automating all paper-based transactions.
An EDI transaction is the direct migration of an application from a desktop in one organization to a computing application in another. EDI automatically determines the document format, so sharing is fast and accurate.
The application of integrated EDI methods to share a wide range of documents is a top choice for businesses and organizations around the world as part of their supply chain and business-to-business networks (B2B).
2. How does EDI work?
EDI transactions are executed according to a pre-set EDI standard. Administrative procedures must be established in accordance with the quality of data to be transacted. Some common standards of EDI such as: ANSI X12, EANCOM, EDIFACT, HIPAA, IDoc, ODETTE, RosettaNet, SWIFT, Tradacoms, VDA,VICS..
Types of EDI transmission:
• Direct EDI aka Point-to-Point EDI
• Value-added network (VAN)
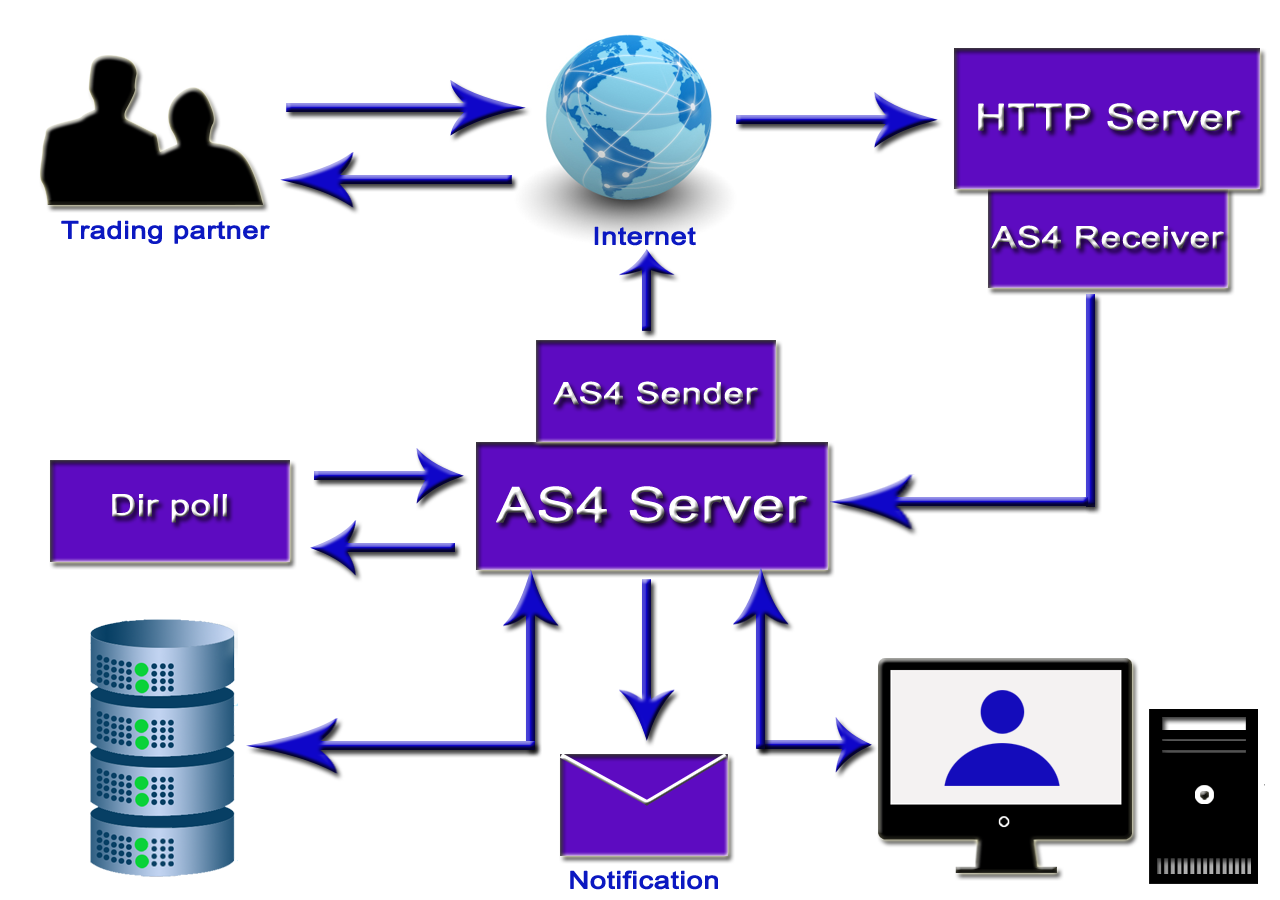
• EDI via AS2
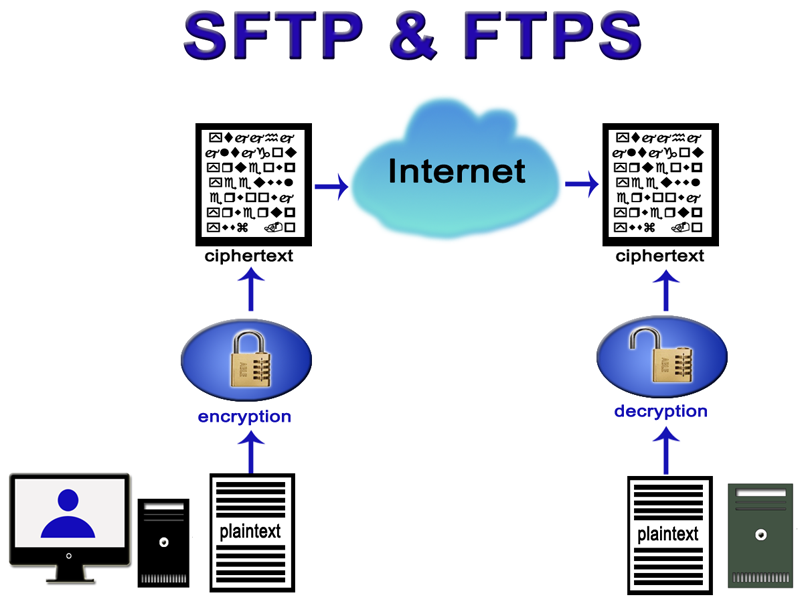
• EDI via FTP/VPN, SFTP, FTPS
• Web EDI
• Mobile EDI
• EDI Outsourcing
• EDI sofware
EDI works on EDI data elements including items such as sender ID, receiver ID ... Data segments can combine two or more related elements to give them greater meaning. A business or transactional process will be clearly described by the EDI the movement of the flow of documents to and from different locations and departments.
3. Benefits of EDI?
In the processes of B2B, EDI transaction is an indispensable important step in data exchange and information transmission between enterprises.
EDI transactions bring a number of key benefits for businesses such as:
• Automate all information exchange activities between businesses: invoices, documents ... help businesses save time and money.
• Safety, accuracy, high performance are EDI solutions for data transmission.
• Minimize data file transmission errors
• Easily traceability of data, helping to store and analyze information accurately and efficiently.
• Standard consistency between business and trading partners.
• Easy integration/automation of any EDI (x12/EDIFACT) data into target Flatfile, XML, JSON and vice versa.