1a. What is SFTP Gateway?
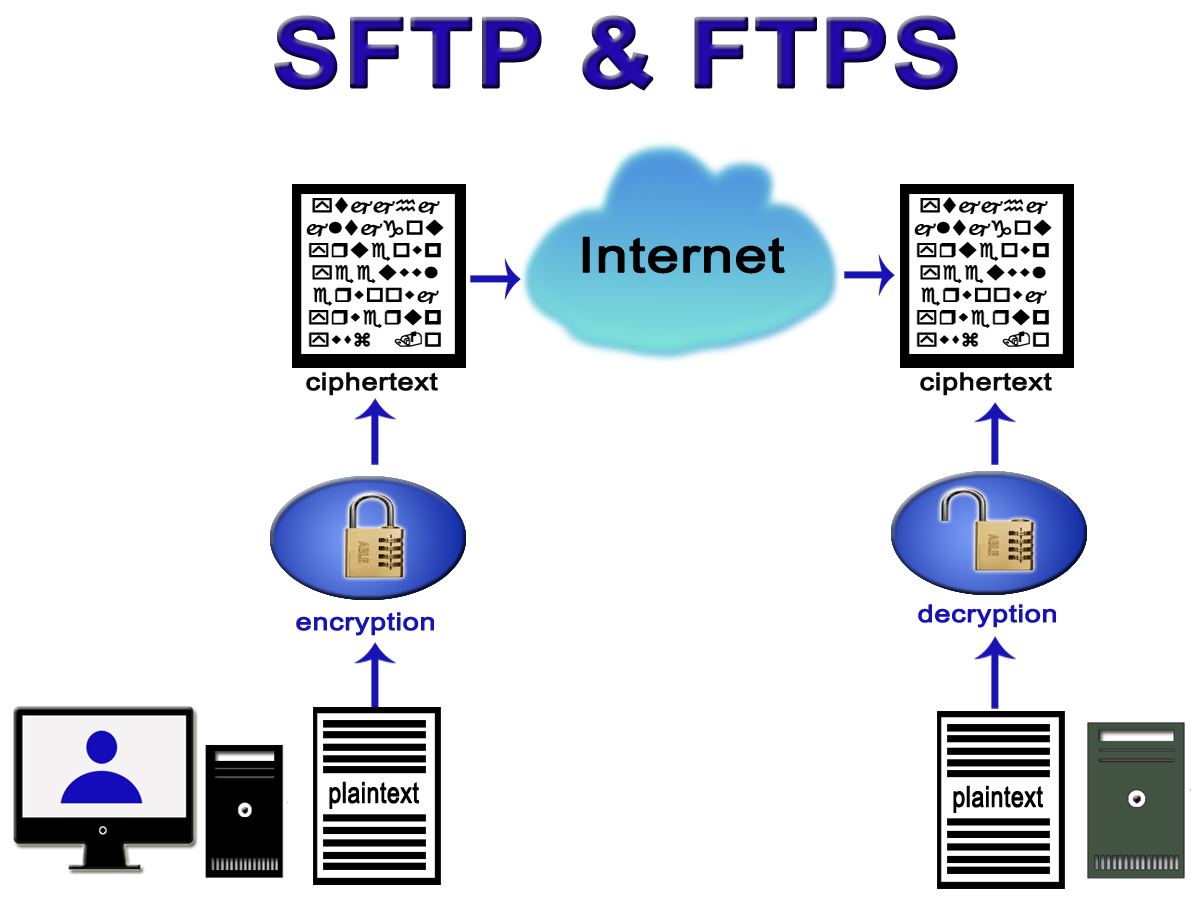
SFTP is the next generation of the File Transfer Protocol (FTP). This is the standard network protocol that’s used for the transfer of files between a client device and a server across a computer network. It’s constructed on a client-server model architecture, which uses separate control and data connections between said client device and server.
1b. How does SFTP work?
SFTP (stands for Secure File Transfer Protocol) is the secure version of file transfer protocol that facilitates data access and data transfer over a secure shell data stream. In simple terms, it’s a tool used to transfer files containing data between organizations. Commonly used by large organizations for tasks like Payroll and pension scheme enrolment, it’s suitable for uploading large files of payment data in standard generated formats such as CSV, XML of Fixed Width.
In the application of SFTP, you have several options to manage the transfer. A cloud-based managed SFTP file sharing solution is a popular choice for businesses. There are two types of solutions you can choose from a public and private cloud SFTP solution.
2a. What is FTPs Gateway?
FTPS (also known as FTP Secure) is an evolution of the widely used File Transfer Protocol (FTP). Because FTP is not typically considered a secure file transfer channel, FTPS was proposed as an alternate in RFC 2228. FTP provides the foundation for FTPS, but the latter includes an additional encryption layer. In FTPS, FTP data travels through the network using either Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols. Therefore it is an alternative to the implementation of the SFTP protocol.
2b. How security works in FTPS?
The operation of the FTPS connection is authenticated with a user ID, password, and a public key certificate (the same way HTTPS works). Key certificates are only required and generated with the permission of tools like OpenSSL. Before connecting to an FTPS server, the FTPS client will be verified for the reliability of the server. Trusted certificate will ensure the reliability and safety of the client when connecting to the server to prevent unauthorized intermediary intrusion.
FTPS (over SSL/TLS) uses X.509 certificates for authentication. These digital certificates include a public encryption key and information about the certificate owner. The public key has two major functions: validation and data encryption. The public key has an associated private key. This private key is stored separately from the certificate, which is used for decrypting the message encrypted by the public key.